SLS 3D printer
Motivation
I used to be a 3D printing enthusiast; I reproduced some open-source FDM printers like kossel in middle school and realized the limitations of FDM 3D printers. I learned that SLS is a high-precision 3D printing method and can even print metal.
So I spent about one year (2017~2018) building a desktop SLS 3d printer all by myself when I was in high school. Although the project looks pretty naive now, the desktop SLS printer with the laser galvanometer had never been presented to the authors’ best knowledge at that time.
Parts
Laser Galvanometer System
The Laser galvanometer works the same as the voltmeter; the volt determines the angle of mirrors that reflect the laser. We use serial to communicate with the computer and receive the GCode(GCode is the most widely used numerical control programming language), process the GCode and plan, calculate the mirrors angle for each movement, use SPI to send the volt data to the DAC module, output the volt and make galvanometer turn to the corresponding angle.
2D Sintering Testing Platform
A 2d testing platform with a stage performance-grade galvanometer from AliExpress was made for single layer sintering. The platform and a nylon sintering test result are shown below.
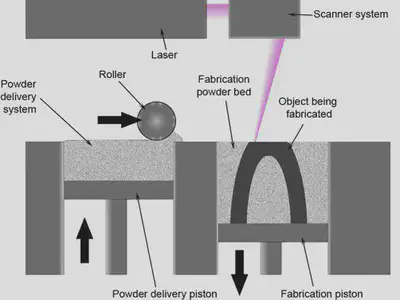
Powder Delivery System
The Powder Delivery System shown below, driven by three stepper motors, spreads the powder evenly over the previous layer. Two pistons store the printed part and the powder waiting to be used respectively.
3D Printer
Combining Laser Galvanometer and Powder Delivery System, we got an SLS 3D printer.

A dry run test video is shown below.
Print result
I added toner in nylon to improve the ability to absorb laser energy, then printed complex geometric mechanisms, 3DBenchy, small chains to test the performance of the printer.
A printing process and small chain videos are shown below.
The printer can print complex structures without support, but the printing of large-scale parts is differential due to preheating the powder uniformly before sintering is very difficult.











